Bitdefender researchers talked about a new modular BHUNT malware that steals the contents of cryptocurrency wallets, passwords and secret phrases.
“BHUNT is a modular styler written in .NET. It is able to extract the contents of wallets including (Exodus, Electrum, Atomic, Jaxx, Ethereum, Bitcoin, Litecoin wallets), passwords stored in the browser, and passphrases obtained from the clipboard,” the experts write.
The new malware is spreading all over the world: in Australia, Egypt, Germany, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Norway, Singapore, South Africa, Spain and the USA. The exact mechanism for delivering malware to users’ machines is still unclear, but experts suspect that hacked installers of various software are used for this.
The use of cracks as a source of infection is not a new trend, for example, earlier in such campaigns, tools such as KMSPico were used to deploy malware.
“The majority of infected users had some form of Windows crack (KMS) on their systems,” the report notes.
The main component of BHUNT is mscrlib.exe, which extracts additional modules that run on the infected system to perform various malicious actions.
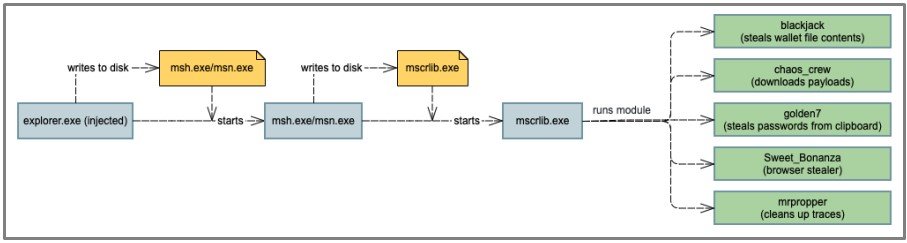
Each of these modules is designed for a specific purpose, from stealing cryptocurrencies to stealing passwords. The following modules are currently included in the BHUNT executable:
- blackjack: steals the contents of the wallet file, encrypts with base 64 and uploads to the server of criminals;
- chaos_crew: loads additional payloads;
- golden7: steals passwords from the clipboard and uploads files to the hacker’s server;
- sweet_Bonanza: steals information from browsers (Chrome, IE, Firefox, Opera, Safari);
- mrpropper: cleans up traces left in the system.
“Although the malware is primarily aimed at stealing information related to cryptocurrency wallets, it can also collect passwords and cookies stored in browser caches. Such data could include passwords for social media accounts, banking, and so on, which could eventually lead to the capture of someone else’s online identity,” the researchers warned.
The company emphasized that the most effective way to protect against such threats is to avoid installing software from untrusted sources and install updates in a timely manner (including for security products).





