Google published a large report detailing a complex hacking operation discovered back in early 2020. The campaign targeted Android and Windows users, and attackers exploited four zero-day vulnerabilities to attack.
The researchers say the attacks they discovered came from two exploit servers (one for Android, the other for Windows) and used a watering hole technique. Such attacks are named by analogy with the tactics of predators that hunt at a watering hole, waiting for prey – animals that have come to drink. This term refers to attacks in which cybercriminals inject malicious code onto legitimate sites that redirects visitors to where the hackers want them.
Both servers exploited vulnerabilities in Google Chrome to gain a foothold on victims’ devices. The attackers then deployed the exploit at the OS level in order to gain more control over the infected device.
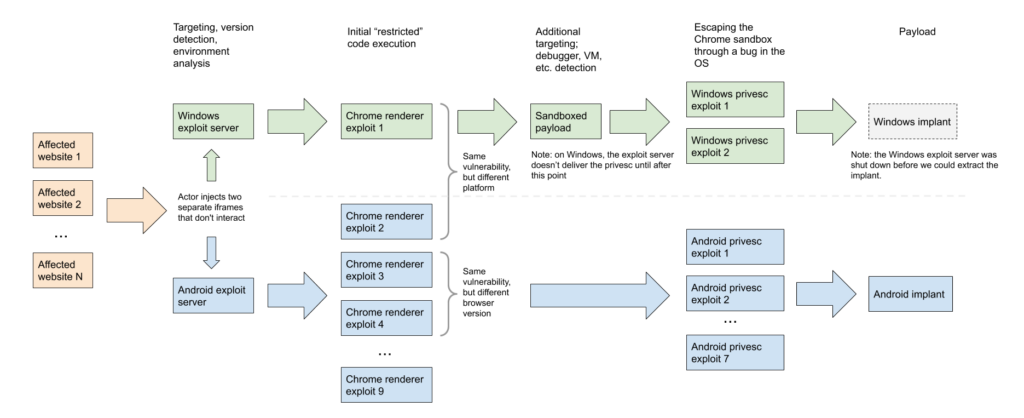
The attacker’s exploit chains were combinations of zero-day vulnerabilities, as well as other recent issues that were already fixed by the developers. So, four errors in Google Chrome were related to the renderer, and one of them at the time of detection was 0-day. In Windows, hackers exploited two zero-day vulnerabilities that allowed them to escape the sandbox. In addition, the attackers had a “privilege escalation suite” of well-known exploits for known vulnerabilities in Android. At the same time, experts note that the hackers, most likely, used 0-day vulnerabilities in Android too, they simply did not store exploits for them on the discovered server.
The four above mentioned 0-day bugs are:
- CVE-2020-6418 – Chrome TurboFan Vulnerability (fixed in February 2020)
- CVE-2020-0938 – Windows font vulnerability (fixed in April 2020);
- CVE-2020-1020 – Windows font vulnerability (fixed in April 2020);
- CVE-2020-1027 – Windows CSRSS vulnerability (fixed in April 2020).
Attackers’ exploit chains are described by experts as tools “designed to be more efficient and flexible through their modularity”.
“This is well-designed, complex code with many new exploitation methods, serious logging, sophisticated and calculated post-exploitation methods, and a lot of anti-analytic and targeted checks. We believe that these exploit chains were designed and developed by teams of experts, ”the report says.
Unfortunately, Google has not yet released any details about the attackers themselves, or about the victims they targeted.





